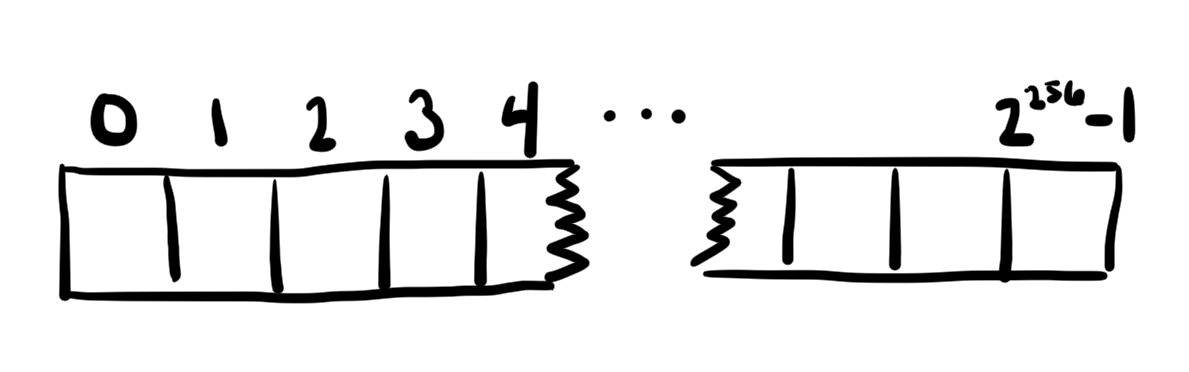Assembly block
Marked by assembly { ... }
pragma solidity ^0.6.1;
contract Hello {
function SayHi() {
assembly {
// assembly code here
}
}
}
Comments
Use the // or /* */ to denote comments
assembly {
// this is a comment
/* this is a multiline
* comment
*/
}
Variables
- Use the
let keyword to declare variables
- Variable is only visible within the block
- Variable will be assigned 0 if not initialized
assembly {
let x := 1
let y // initialized to 0
}
// x and y not visible here
Literals
- decimal or hexadecimal
- strings up to 32 characters
assembly {
let a := 2
let b := 0x03
let c := "hello world"
}
Function
- Take arguments from stack and put results on stack
- Can return multiple values:
let a, b := f(x)
function callF(uint input) public pure returns(uint x, uint y) {
assembly {
function f(val) -> a, b {
a := add(val, 1)
b := val
}
x, y := f(input)
}
}
If
- Conditionally execute code
- No
else block
if eq(value, 0) {
value := 3
}
Switch
- Similar to
if, but with more branching options
- Fallback or default case:
default
- No fall through to following cases
assembly {
switch x
case 0 { x := 1 }
default { x := add(x,1) }
}
Loop
- Repeat operations
break: exit the Loopcontinue: skip to next iteration
function lo(uint max) public pure returns(uint result) {
assembly {
for { let i := 0 }
lt(i, 20)
{ i := add(i, 1) } {
if lt(i,3) { continue }
if gt(i, max) { break }
result := add(result,1)
}
}
}
OpCode
OpCode (Operation Code) is a machine instruction that specifies the operation to be performed - Wikipedia
extcodehash
- Used in openzeppelin IsContract()
utilitity
- Returns the code hash of a contract
assembly { codehash := extcodehash(accountAddress) }
### Data Sanity
- If you access variables of a type that spans less than 256 bits (e.g. uint64, address, bytes16 or byte),
bits not part of the type, may not be `zeroed`
- Always clear data before using it
```
uint32 x = f();
assembly {
x := and(x, 0xffffffff)
/* now use x */
}
```
### Two's Complement
- Used in EVM
- Same arithmetic for signed and unsigned
- No negative 0
### Signed Functions
- Use to process signed data
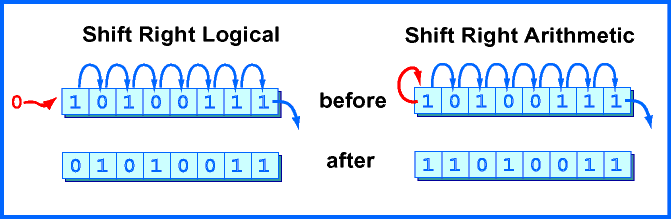
- sdiv(), smod(), slt(), sgt(), sar(), signextend()
- Would x be 100 or 99 from the following code?
```
int a = -3;
assembly {
let x := 100
if lt(a, 0) {
x := 99
}
}
```
State Variables Storage Layout
- One Astronomically large array
- Solidity generates code that saves variable values in their declaration order.
- Variable first was declared first, it’s stored in slot 0
- Items that need less than 32 bytes are packed together. See Rules
contract Sample {
uint first; // storage slot 0
uint second; // storage slot 1
}
Astronomically large array mental model
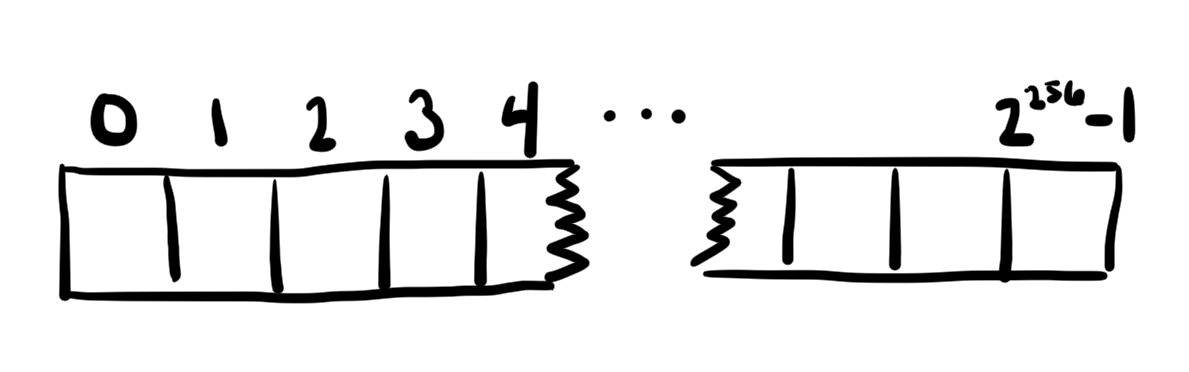
Memory Example
function getData(uint value) public view returns (bytes32 output) {
assembly {
function allocate(length) -> pos {
let freePointer := 0x40
pos := mload(freePointer)
mstore(freePointer, add(pos,length))
}
let dataSize := 0x20 // 32 bytes
let offset := allocate(dataSize)
mstore(offset, value)
return(offset, dataSize)
}
}
Calldata demo
// return calldata as bytes output
function getData(uint input) public view returns (bytes memory output) {
assembly {
let base := mload(0x40)
mstore(add(base, 0x00), 0x20) // pointer to data
mstore(add(base, 0x20), 36) // data length
calldatacopy(add(base, 0x40), 0, 36) // data from byte 0
return(base, 0x80)
}
}
Storage demo
uint8 data1 = 1;
uint8 data2 = 2;
uint8 data3 = 3;
uint8 data4 = 4;
// get data3 and return it as ouput
function getData() public view returns(bytes32){
assembly {
let data := sload(data3_slot)
let result := and(shr(shl(3,data3.offset), data), 0xff)
mstore(0, result)
return(0,32)
}
}